Hi Dirk,
nice to have you around, welcome to GNU Radio! I don't know your
level of DSP knowledge, so please excuse if I either throw too
many high-level concepts at you or assume you could want to read
up on something that you already know. If something in my reply is
unclear, please don't hesitate to ask for clarification.
So, my understanding is that your SDR device first downconverts your 150.22 MHz signal to complex baseband, is that right?
So, what is the objective here? You say you need to /detect/ the pulse, but for what purpose? Is it just about detecting the presence of the pulse, or is it used for eg. time detection?
Your filter->decimate approach sounds very reasonable; I'm not 100% convinced by using the FFT for something that is concentrated in *time* domain, but that might depend on the purpose mentioned above.
I'm not sure I understand the question. An FFT is simply an DFT. It's a mapping of N-dimensional vector to N-dimensional vector,2) Im somewhat confused about the FFT block if I just pipe the SDR straight into it. The FFT size is set to 1024 and the window is set to "window.blackmanharris(1024)". So Im assuming the FFT just applies one window (?) and outputs 1024 bins. However, how many samples are accumulated before the FFT is run? I would have assumed I can control that too. And if so, should I best be doing this every 50ms, 500ms, 2000ms, ..?
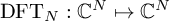 . The window is multiplied
point-wise with the input vector prior to the DFT to avoid
spectral leakage.
. The window is multiplied
point-wise with the input vector prior to the DFT to avoid
spectral leakage.
There's no accumulation involved anywhere.
Maybe, or maybe the spectrum sink really isn't the right tool to visualize a pulse! Again, we might want to discuss what this pulse is and what it's used for.3) I can use the rational resampling block to bring the sample rate down to 48khz so I can use the audio sink. From that I can still hear the pulse even if it is not visible in the spectrum (gui sink). Im assuming this is just because the plotting cannot keep up?
Hm, but correlating a signal with a known fixed sequence is, mathematically, a convolution.4) In the time domain I guess I can generate a synthetic pulse of the same length / frequency and then cross correlate.
That is identical to doing FIR filtering – in fact, if we
consider the shape of your pulse as what is often referred to as pulse
shape filter, then that filter in the receiver would simply
be the matched filter to that.
"Continuous" would mean you'd do an infinite-length correlation, so that's not 100% possible.Not obvious to me how to generate the required pulse in gnuradio though (would a continuous signal work?).
Hm, but an autocorrelation would take a complete signal, shift it by all possible shifts and calculating the dot product between the shifted version and the unshifted, right? That would require to have the complete signal at once.I also notice there are no built in (auto)correlation blocks?
But GNU Radio is a streaming architecture, so that can't work.
You can implement a limited-length
autocorrelation/crosscorrelation relatively easily; we can talk
about how that would look like, but my gut feeling is that this
might be something that might not make too much sense in your
specific use case.
As a gut feeling: you don't really care about whether the pulse is exactly at a certain frequency (it's absolutely not normal for wireless receivers to know the exact frequency a priori), but when it happens. So we might want to discuss the kind of pulse, and kind of noise we're talking about.I found the "correlation estimator" but not clear how to use it. As for dealing with the frequency uncertainty problem. Does one just try correlating with different freuencies and pick the best one? Or what is the good thing to do here given I may also have to deal with quite a bit of noise.
As a further gut feeling: I think your autocorrelation question indicates you might be on a very good track – it's possible cyclostationary estimation methods might be helpful here.
Best regards,
Marcus
Fist of all, while Im a newbie to (gnu)radio, congrats to the dev team for a great piece of software. My question is about the need to detect a weak, noisy, short (10ms) pulse that occurs every 1.5 seconds. It is transmitted at a particular frequency (e.g., 150.22 MHz) but in practise I have found this can vary by as much as +/- 500Hz. There is no modulation, it is simply an on/off keyed pulse. Say I have an SDR generating data at 2.5 MSPS. I have so far been experimenting with standard scipy/numpy routines to collect a batch of samples, perform a FFT (freq domain) and do a cross correlation (time domain). However, Im by no means a dsp guy and would like to leverage gnuradio as much as I can. I have been poking a bit but have some basic questions. 1) 2.5 Msps gives me way more bandwidth than I neeed. Assuming, for now, I only care about a single pulse frequency I really only need ~1khz bandwidth. In the frequency domain I can directly decimate down (with a big factor) to the 1-2 khz range using the low pass filter block, do an fft, and look for peaks. Is that the right approach? 2) Im somewhat confused about the FFT block if I just pipe the SDR straight into it. The FFT size is set to 1024 and the window is set to "window.blackmanharris(1024)". So Im assuming the FFT just applies one window (?) and outputs 1024 bins. However, how many samples are accumulated before the FFT is run? I would have assumed I can control that too. And if so, should I best be doing this every 50ms, 500ms, 2000ms, ..? 3) I can use the rational resampling block to bring the sample rate down to 48khz so I can use the audio sink. From that I can still hear the pulse even if it is not visible in the spectrum (gui sink). Im assuming this is just because the plotting cannot keep up? 4) In the time domain I guess I can generate a synthetic pulse of the same length / frequency and then cross correlate. Not obvious to me how to generate the required pulse in gnuradio though (would a continuous signal work?). I also notice there are no built in (auto)correlation blocks? I found the "correlation estimator" but not clear how to use it. As for dealing with the frequency uncertainty problem. Does one just try correlating with different freuencies and pick the best one? Or what is the good thing to do here given I may also have to deal with quite a bit of noise. Any guidance appreciated. Many thanks, Dirk _______________________________________________ Discuss-gnuradio mailing list address@hidden https://lists.gnu.org/mailman/listinfo/discuss-gnuradio